What is optical filters
Fluorescence filter is a fluorescence imaging filter for biomedical and life science instruments, the key components, the main role is in the biomedical fluorescence analysis system for the separation and selection of substances in the excitation and emission fluorescence Of the spectral characteristics of the band. It is usually required that the filter cut-off depth be greater than OD5 (optical density, OD = -lgT). The core requirements for filters used in fluorescence detection systems are high cut-off steepness, high transmittance, high positioning accuracy, high cut-off depth, and excellent environmental stability.
Fluorescence filter is a combination of three, three are excitation filters, emission filters and dichroic filters.
Excitation Filter (Exciter Filter, Excitation Filter, Excitation Filter): In the fluorescence microscope, only the excitation wavelength of the filter can pass through the fluorescence. In the past, a short-pass filter was used, and now a band-pass filter is basically used. The housing is marked with arrows indicating the direction of propagation of the recommended light.
Emission Filter (Emitter Filter, Emitter): Select and transmit the fluorescence emitted by the sample, the other range of light cut-off. The wavelength of the emitted light is longer than the wavelength of the excitation light (closer to red). A band-pass filter or a long-wave-pass filter may be selected as the emission filter. The housing is marked with arrows indicating the direction of propagation of the recommended light.
Dichroic Mirror (Dichromic Beamsplitter, Dichromatic Beamsplitter): also known as dichroic mirrors or dichroic mirrors. And placed at an angle of 45 ° to the optical path of the microscope. This filter reflects one color of light (excitation light) and transmits another color of light (emitted light), the reflectivity of the excitation light is greater than 90% and the transmittance of the emitted light is greater than 90%. The impervious portion of the spectrum is reflected rather than absorbed. Filter in the transmitted light and reflected light color complement each other, and thus also known as dichroic filters.
Our optical filters are designed for fluorescence imaging applications, with durability in mind and high-performance optical specifications in manufacturing. The filter substrate is made of quartz, which can achieve 1/10 lambda surface accuracy, while the thermal expansion coefficient of quartz is relatively small, can obtain higher image quality.
We equipped with 4 coating chambers to provide various filters to our customers. For custom specifications, please talk to our coating engineers, we are more than happy to simulate the coating result for you. Contact us today, and find out our coating capability for your needs.
Band pass filter can separate a band of monochromatic light, the ideal transmittance of band-pass filter through the bandwidth is 100%, while the actual band-pass filter pass band is not the ideal square. The actual band-pass filter generally has a center wavelength λ0, a transmittance T0, a half width of the pass band (FWHM, a distance between two positions where the transmittance in the pass band is half the peak transmittance), the cutoff range and other key parameters to describe.

Multichannel filters differ from conventional bandpass filters by allowing only one continuous band of light to pass through it, allowing two or more bands of light to pass through.
Multi-channel filters can be achieved on a filter to achieve the need for multiple general filter stack to achieve the effect, making the design more compact, and can reduce costs.
This filter in the optical communications, infrared and medical applications have a wide range.
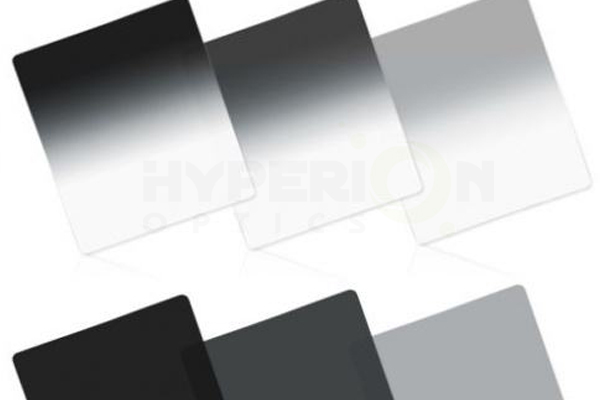

Neutral gray-scale filter is a non-selective filter, that is, ND mirror for a variety of different wavelengths of light to reduce the capacity is the same, uniform, only to weaken the role of light, and The original color of the object will not have any impact, so you can reproduce the real scene contrast.
The main purpose of using ND mirrors is to prevent over-exposure.
For example, when you want to extend the exposure time when the light is strong, use the ND lens to reduce the light entering the lens, you can use a slower shutter shot. For example, in the daytime when the light is strong with slow shutter speed to capture the waterfall to show the virtual effects of water and other special effects, you need ND mirror.
Labels: filters, Fluorescence filter, glass filters, Hyperion, interference filters, optical filters, optics, optics china, spatial filtering

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home